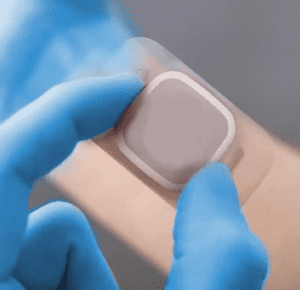
Selecting the correct adhesive for your wearable medical device is crucial to its market success, but with so many adhesives available to the medical market it’s difficult to know where to start!
So, you have a concept, you even have the design, but now it’s time to start making decisions about the materials and the vast range of adhesives seems like a daunting landscape to navigate.
When considering the correct adhesive for your wearable device it’s important to review some key factors to identify the right materials for you. For example, when the adhesion is too low, the device may not stay in place long enough for the full therapeutic effect but if it adheres too well, the tape may cause some mechanical trauma at the time of removal, so let’s review some of the key considerations of your device;
1. Skin compatibility:
Our skin is the first line of defence, it’s designed to recognise intruding organisms and substances and act fast, that’s why it’s so important you choose an adhesive that’s safe for human skin, medical adhesives are designed specifically to work with our largest organ and not cause any irritation or allergic reactions. There are a wide range of suppliers that develop medical grade adhesives specifically for such applications, such as 3M, Avery Dennison, Flexcon and many more! These materials will be rigorously tested in biocompatibility compliance in accordance with regulatory guidelines such as FDA and CE Marking.

2. Adhesion strength:
The adhesive should have sufficient adhesion strength to keep the wearable device in place during the intended use. This doesn’t always mean long term wear, some wearable devices may only require short term wear, and the ability to reposition the device may be a key requirement. So, when choosing an adhesive for your device be sure to not only consider the strength of the adhesive but also the ease of removal; high trauma removal, a tacky residue on the skin, or the use of an adhesive that cannot be repositioned may be detrimental to the device’s success.

3. Duration of wear:
The adhesive should be able to maintain its adhesion properties for the intended duration of wear. For instance, if the device needs to be worn for an extended period, the adhesive should be able to provide long-term adhesion without causing skin irritation, with adhesive tapes such as 3M™ Medical Tape 4578 for up to 28 days wear time & Avery Dennison MED 3046 approved for up to 21 days wear-time there are outstanding suppliers to choose from. Alternatively, the device may be designed for short term wear, so you want to choose an adhesive that will be easy to remove after a short period of time materials like the dermaFLEX™ NNRU by FLEXcon.

4. Water resistance:
Wearable devices that are designed for long term wear must be designed with a user’s day to day routine in mind, and often this includes exposure to water, sweat or other liquids, take for example a Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) the user may wear the device for up to 14 days, during this period its important the adhesive should be water-resistant to prevent detachment or interference from sensor readings. Does the adhesive withstand chlorinated, or even salt water? A simple requirement for a user that may wear the device for sport, or while vacationing.

5. Conformability:
In an average day the human body is constantly moving, and our bodies largest organ – the skin, changes temperature, perspires, withstands friction from clothing and sheds dead cells all of which can be a tricky surface for an adhesive, your chosen material should be able to conform to the position on the body to ensure proper placement and prevent discomfort during daily activities. The placement of your wearable device will play an important role in the adhesive you choose. For example, a device that will be positioned at the back of your arm may require a different adhesive to a device that’s positioned on your chest.

6. Manufacturing process:
The adhesive should be compatible with the manufacturing process of the wearable medical device. Some adhesives may require a specific temperature or humidity range during manufacturing or require the integration of a flexible printed circuitry. Others may need to withstand sterilization processes, such as gamma irradiation, ethylene oxide, or steam. A flexible material converter would be able to advise you on the best combination of materials required for optimal device performance, high volume manufacture, and best ways to reduce material wastage.

PolarSeal works closely with suppliers across all industry sectors, we can aid you in the selection of your materials to ensure the optimal adhesive for your product functionality. Our advanced knowledge of manufacturing and engineering alongside end-user requirements and that of our partners, means that we will be able to identify the optimal medical adhesive and material combination for your product.