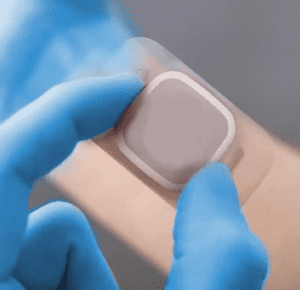
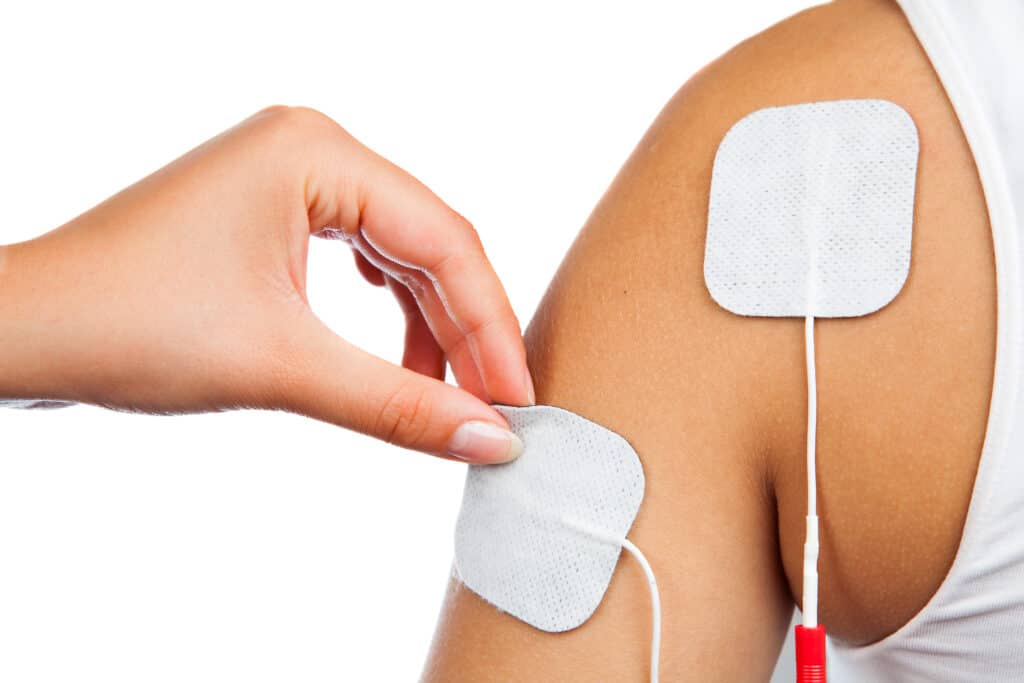
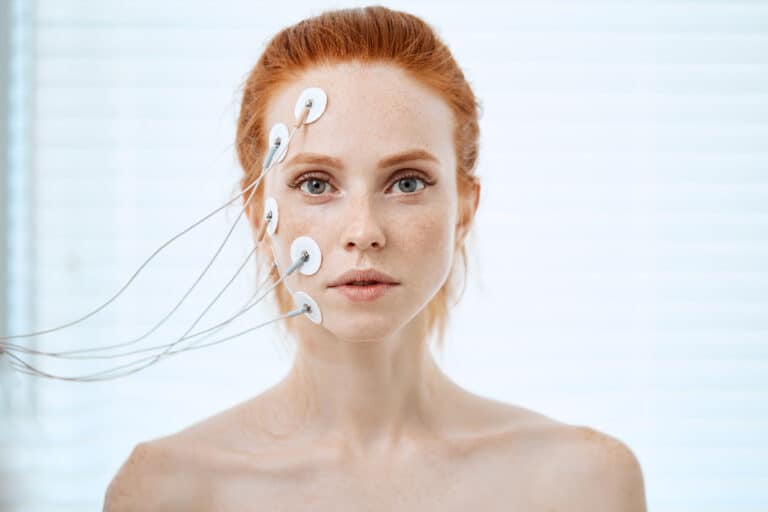
Electrode sensors are used in various medical applications to measure electrical signals from the human body to investigate and diagnose a variety of medical conditions. The use of electrode sensors is a rapidly advancing diagnosis tool, designed to measure electrical activity within the body ranging from vital organs like the heart and brain, to electrical signals to specific muscle groups;
Electrocardiography (ECG/EKG): Measuring the electrical activity of the heart. ECG/EKG tests are commonly performed to diagnose heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and heart failure.
Electroencephalography (EEG): EEG measures the electrical activity of the brain. Electrode sensors are placed on the scalp to record the brain’s electrical activity and used to diagnose conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries.
Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles. Electrode sensors are placed on the skin or inserted directly into the muscle to record muscle activity aiding the diagnosis of conditions such as muscle disorders, nerve damage, and spinal cord injuries.
Electroretinography (ERG): ERG measures the electrical activity of the retina. Electrode sensors are placed on the cornea or skin around the eye to record the electrical response of the retina to light to diagnose retinal disorders and diseases such as macular degeneration.
Electrodermal activity (EDA): EDA measures the electrical activity of the skin. Electrode sensors are placed on the skin to measure the skin’s electrical conductance, which is affected by sweat gland activity. EDA is used for lie detection tests and to diagnose conditions such as anxiety disorders.
Bioimpedance measurements: Electrode sensors are used to measure bioimpedance, which is the electrical resistance of body tissues. Bioimpedance measurements are used to assess body composition, fluid status, and cardiac function.
Electromedical devices are also used to treat and manage a wide range of medical conditions on a long-term basis, improving patient outcomes and quality of life for people living with life long conditions, from pain management devices such as a TENS to alleviate pain caused by conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and nerve damage, to Deep brain stimulation (DBS) used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.

Quality of life for patients living with Epilepsy, Cardiac arrhythmias & Sleep apnea is improved by the use of electromedical devices, a matter of huge importance when developing an Electromedical device is the comfort of the user, the wearability has an enormous impact on the quality of life for the end user. For some conditions, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGM) for Diabetes patients will wear the device every day of their lives, so when developing an electromedical device there are many specific requirements that you should consider;

Safety & Regulatory
Safety is paramount when designing an electromedical device. The device must be designed to minimize the risk of harm to the user, including the risk of electrical shock, burns, and other injuries. Electromedical devices are subject to regulatory requirements from agencies such as the FDA. The device must be designed to meet these requirements and be approved for use.

Reliability & Durability
Devices may be worn intermittently for immediate pain relief, such as a TENS machine, or as a diagnostic tool such as an ECG, in instances like these the device must be easily removed and repositionable as well as have the ability to conduct and receive an electrical current. It would also need to be storable once removed from skin. Other devices may require longer wear time, for example an ambulatory EMG or CGM, these devices must be durable, waterproof and be able to withstand perspiration, the adhesion should be designed to enable the patient to go about their usual day to day routines.

Conductivity
Electromedical devices may need to be integrated with other medical devices or systems. The device should be designed to facilitate interoperability and data exchange.

Cost
The cost of the device is an important consideration, as it can impact the device’s accessibility and affordability for patients and healthcare providers.
PolarSeal can aid the development of your device and guide you through the above considerations. PolarSeal proudly partner with a wide range of material manufacturers and will carefully consider the requirements of your medical device enabling us to pair your device with the perfect adhesive material.