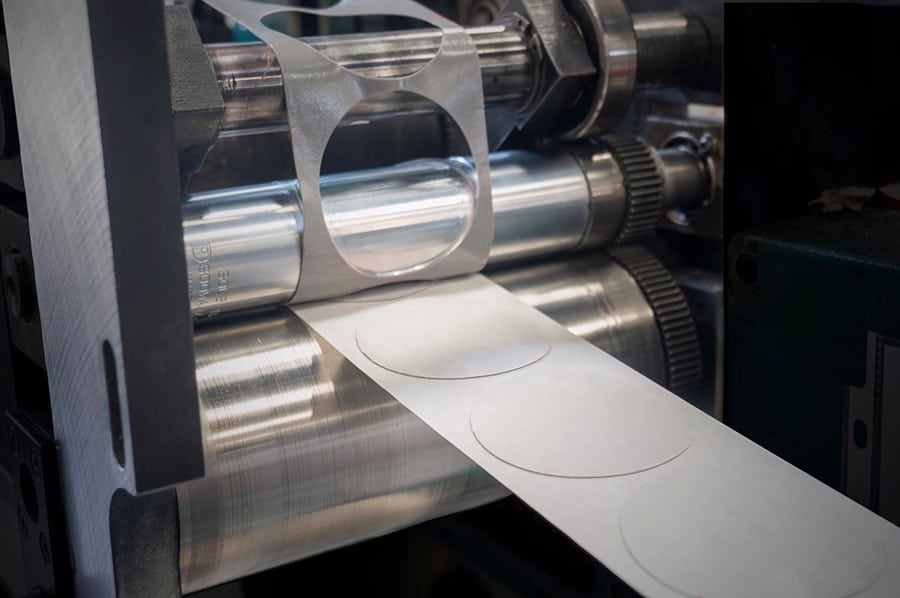
Die cutting is a technique utilised in a vast range of manufacturing industries and can be an expensive process if not monitored or optimized for maximum efficiency. It is important to consider the many factors that can alter the overall cost when incorporating die cutting into your material conversion process. The use of die cutting for mass production of component parts can save medical device companies sizeable sums by implementing process changes, material efficiency alterations, and streamlined operations to name a few. When reviewing your die cutting process there are a range of ways to reduce short term and long-term costs.
1. Material Efficiency
Cost Implication – Traditional cutting methods like laser cutting or manual cutting can generate more waste due to their less precise nature and waste material can accelerate the costs of your production due to increase spend on raw materials, through to waste disposal and recycling. Some methods may not maximise the usage of the material provided, making each part produced more expensive.
Resolution – Die cutting is a highly precise process that allows for minimal material waste. It uses a custom-made die to cut the material (often sheets or rolls) into specific shapes and can maximize the full width and length of the materials used, converting maximum parts per roll as possible, as well as reducing total waste.
2. High Speed Production

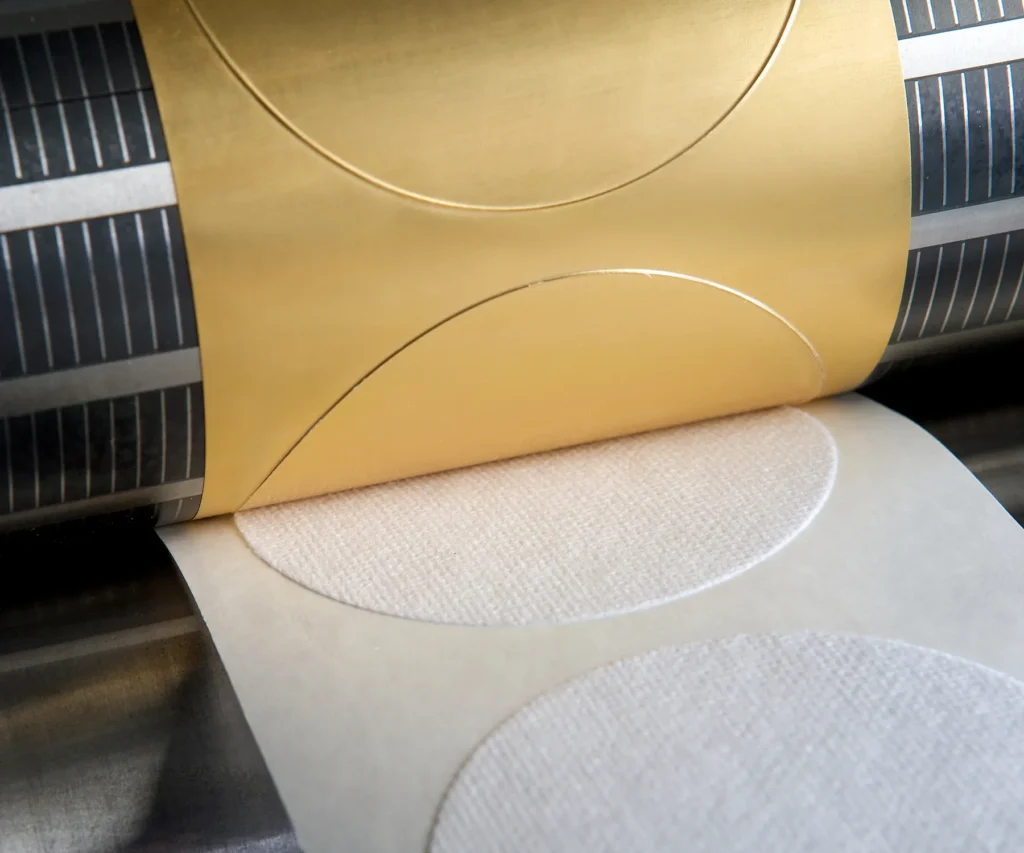
Cost Implication – Manual die cutting and prototyping can be a laborious task, whether it be handheld tooling or plotter cutting, the cost implications of labour are high, raising the overall costs of part production, as well as time to completion being extended.
Resolution – Rotary die cutting is a fast and efficient process integrating multiple stages into one streamlined production line. It can produce thousands of components in a short amount of time and maximizing parts be metre, which can lead to reduced labour costs and increased production output compared to manual cutting and due to its semi-automated nature, it requires fewer manual interventions. However, maintenance is key as down time can have a severe negative impact of manufacturing KPI’s.
3. Consistent Quality
Cost Implication – Quality is crucial when it comes to medical device manufacturing, even small variations in size, shape and variable text are unacceptable. As a result, rejects can raise the total cost of your project. Not only is a rejected part a waste of material, but it is also a waste of labour and production time as well as all departments of the business. This also extends the Go to Market (GTM) time frame, having an extensive impact on the business as a whole and its financial performance.
Resolution – A refined and validated die cutting process offers high level of precision and consistency coupled with automated vision systems. Consistent qualitative outcomes help in minimizing rejected parts and the associated costs, the process can often eliminate the need for secondary operations like trimming or finishing. This further reduces costs and production time.
4. Customisation and Complexity
Cost Implication – Custom designs are part of the design process, but intricate designs and shapes can be time consuming to produce and when cut manually the risk of imperfections and inconsistencies are increased. Intricate shapes of parts that differ from market normality require technical drawing reviews, as well as expensive tooling to cut out. Technical design also tends to increase wastage of resource, material and other variables during manual processes.
Resolution – The usage of die cutting allows for intricate shapes and designs to be cut out with precision and maximizing the part volume against the meterage of material used. This is especially valuable in the medical industry where devices can have complex shapes such as fixation devices that hold multiple tubes in place. Custom dies can be created to suit the specific needs of a device and adhesive patch. While creating the initial die might have some associated costs, it’s a one-time investment. Once the die is made, it can be used repeatedly, reducing the overall tooling costs over the long term. However, depending on volumes manufactured, the tooling may need resharpening, this can result in down time, so having 2 tools is sometimes advisable.
5. Scalability
Cost Implication – When you opt not to utilise die cutting, scalability will always be limited and manual labour can only be ramped up by adding more labourers, which again incurs additional labour costs. Sheet to sheet methods of cutting is only setup up to generate lower volumes, with some machinery and processes not being capable of fulfilling sheet to roll or roll to roll, which has higher volume output potential.
Resolution – Rotary die cutting is easily scalable. Once the die is created, the production process can be quickly ramped up to meet increased demand without significant lead time or setup costs. Depending on the run speed of your converting line, rotary die cutting can produced 100’s – 1000’s of parts a minute while some other cutting methods will achieve 1 third of that output.
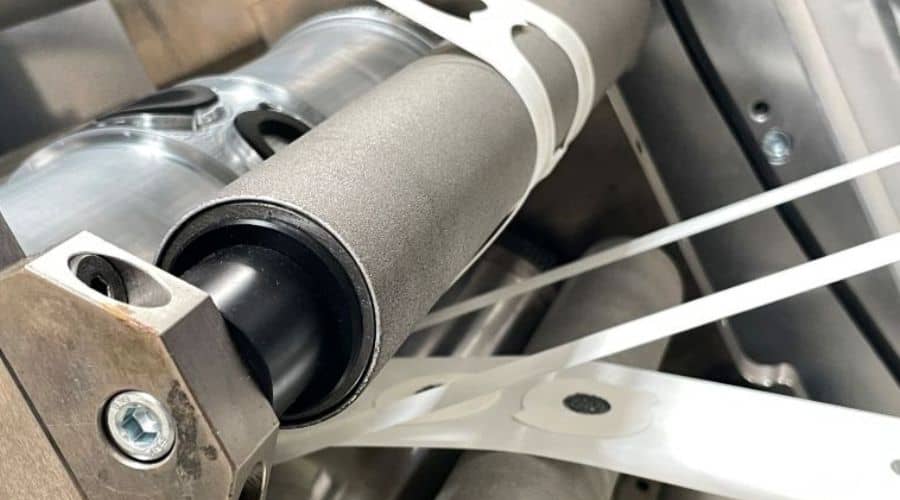

6. Versatility in Materials
Cost Implication – When cutting materials your range may be limited due to the difficulty of working with more robust or thicker materials, restricting the development of your device. Cutting through these materials even more so after lamination of several layers, can wear down tools quickly and consume time and resource when done manually.
Resolution – Die cutting can be used on a wide range of materials including plastics, rubber, foam and adhesives. This versatility allows for the selection of cost-effective materials without sacrificing quality. Note, that depending on the intended outcome of your die cutting process and the component parts that are produced, you may require bigger tools, more frequent tool sharpening, and more management to ensure the process is as efficient as possible.
7. Regulatory Compliance
Cost Implication – Gaining the necessary regulatory approvals is a time-consuming process and many factors can cause delays, or even hinder your chances of approval. Bioburden, imperfections and inconsistencies can all limit a medical device designers chances of regulatory approval.
Resolution – Die cutting can help in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. The precision and consistency of die-cut components, combined with the controlled manufacturing environment can contribute to meeting the strict requirements of the medical industry.
Overall, die cutting provides a cost-effective and efficient solution for producing precise and complex components, making it a valuable method for medical device creators looking to save money in their manufacturing process. However, it is important to recognise that these suggestions may require a change in some of your processes and workflows, working with an experienced flexible material converter can help to streamline your processes and upscale the production of your medical device or parts.
Read More from PolarSeal

Your Rotary Die Cutting Questions Answered
There are a wide range of capabilities when it comes to die-cutting, at PolarSeal we are equipped and experienced on many of these, from Flat

4 Key Factors That Affect the Cost of Die Cutting
Cost is top of mind when clients are looking to flexible material converters to manufacture a die cut device or component to take to market.

Guide to Die Cutting in Medical Conversion & Manufacturing
Die cutting in medical conversion and manufacturing can enhance the quality of parts and production by providing better precision, minimising waste, creating consistency and improving